This entry gives more quantitative information on the diagonalization reported in klog 22433 (wrongly filed in BS section originally).
The tasks that were done were these:
- Sensor diagonalization from L and T to Y using the L and T resonance frequencies and
- Actuator diagonalization using DC actuation.
Sensor diagonalization between L and T is challenging because the resonance frequencies are very close to each other around 70 mHz. Therefore, did the diagonalization from L and to Y, as written above.
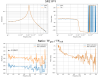
As can be read the from the results below, the coupling from L and T into other DoF decrease, however, the coupling from Y to L and T, increased at the resonance frequencies of L and T. Namely, from Y to L is 3% of L, and from Y to T is 20% of T.
Actuation coupling of 20% from Y to T is large, and I should probably revert the matrices to the previoius geometrical values.
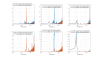
Quantitative results
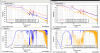
Coupling from L to T and Y
- Along T: improvement at low frequencies by a factor of 8.2.
- Along Y: improvement at low frequencies by a factor of 6.4, and at the resonance by a factor of 3.7.
- See Fig. 1: before (left) and after (right) diagonalization.
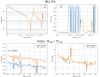
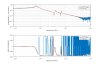
Coupling from T to L and Y.
- Along L: improvement at low frequencies by a factor of 6.3.
- Along Y: no improvement at low frequencies, and an improvement at the resonance by a factor of 1.2.
- See Fig. 2: before (left) and after (right) diagonalization.
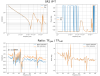
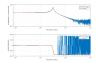
Coupling from Y to L and T
- Along L: increase at low frequencies by a factor of 3.9 and by a factor of 1.2 at the resonance.
- Along T: increase at low frequencies by a factor of 3.1, and an improvement at the resonance by a factor of 1.2.
- See Fig. 3: before (left) and after (right) diagonalization.